What Did The Government Do About The Stock Market Crash In 1929
New York TimesFrom Black Tuesday Oct. October 22 The government of Aristide Briand falls in France.
 Stock Market Crash Facts Causes Effects Predictions
Stock Market Crash Facts Causes Effects Predictions
The Wall Street Crash of 1929 also known as the Great Crash was a major American stock market crash that occurred in the autumn of 1929.

What did the government do about the stock market crash in 1929. Recovery From 1929 Crash Was Quicker Than Most People Think. However as a result of Hoovers philosophy the government stayed uninvolved in the fiasco for years. High unemployment and an unregulated unsustainably high stock market led to a collapse in confidence which caused the stock market crash.
The 1929 stock market crash didnt help but for some reason its come down to us that the stock market crash started the Depression when theres a lot of evidence against that theory. Overall the stock market crash of 1929 represented the worst market downturn in US. 13 1929 30 billion simply vanished from the United States economy due to falling stock prices source.
Federal Reserve leaders differed on how to respond to the event and support the financial system. The Roaring Twenties roared loudest and longest on the New York Stock Exchange. Today we know much more than they did nearly a century ago when the stock market crashed.
The initial decline in US. In October of 1929 the stock market crashed wiping out billions of dollars of wealth and heralding the Great Depression. However as a singular event the stock market crash itself did not cause the Great Depression that followed.
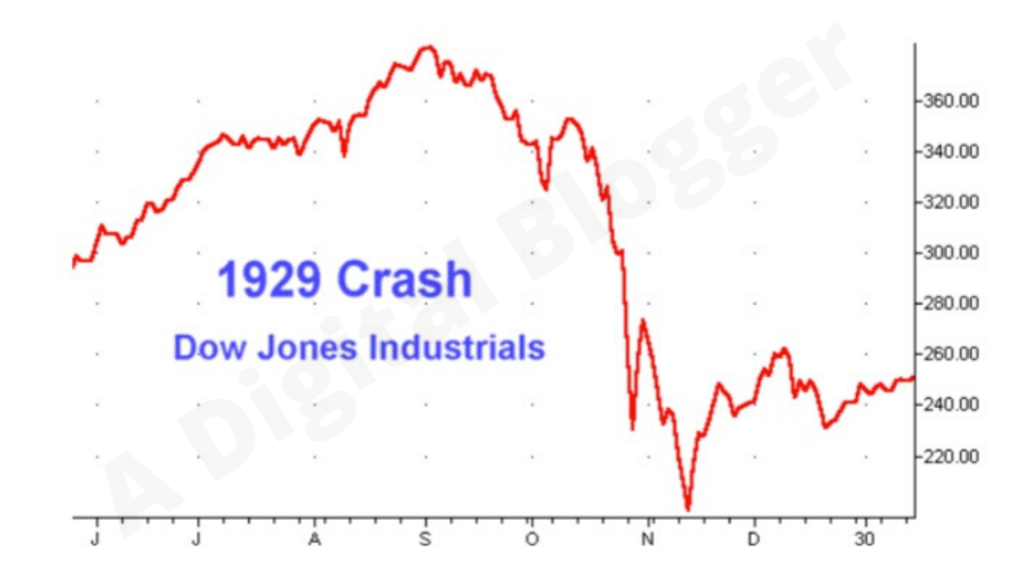
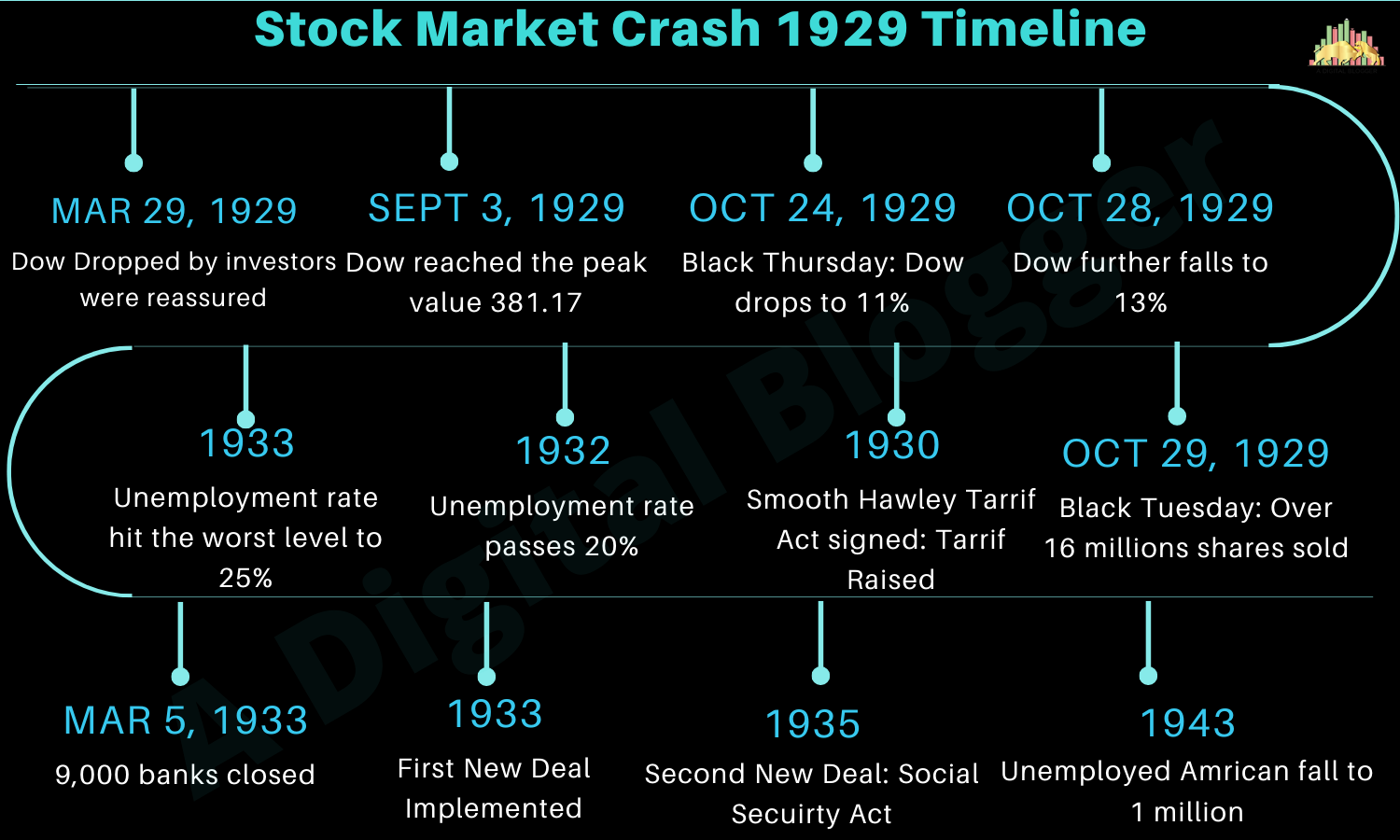
As a stock market historian the single best benchmark for all market analysis is the years from 1929 to 1954. The promise of the Hoover administration was cut short when the stock market lost almost one-half its value in the fall of 1929 plunging many Americans into financial ruin. Known as Black Thursday the crash was preceded by a period of phenomenal.
In 1929 a stock market crash caused the Dow Jones index -- one of the main indices used to evaluate the health of the American economy -- to lose nearly 12 percent of its value in one day source. Lessons Learned from the 1929 Stock Market Crash. When the stock market crashed in late 1929 the initial belief among economists was that the economy would quickly bounce back from its drop.
When that did not occur Hoover supported the. 29 1929 to Nov. It started in September and ended late in October when share prices on the New York Stock Exchange collapsed.
This is the period when. A position in bonds probably wouldnt have shielded you completely from stock-market losses but it certainly would have softened the blow. 4 always-good pieces of advice.
Output in the summer of 1929 is widely believed to have stemmed from tight US. In September 1929 the Dow Jones Utility Average DJUA hit its peak at 145. After the 1929 stock market crash trading days were cut back from six to five as one way to prevent another collapse.
Stock Market Crash of 1929. October 2429 Wall Street Crash of 1929. Monetary policy aimed at limiting stock market speculation.
The government raised interest rates. Roosevelts intervention after the stock market crash of 1929 was followed by the Great Depression of the 1930s with its massive and long-lasting. Chances are that it is quite unlikely.
It took traders and investors time to adjust to a shortened trade week but. The 1920s had been a prosperous decade but not an exceptional boom period. Three multi-digit percentage drops wipe out more than 30 billion from the New York Stock Exchange 10 times greater than the annual budget of the federal government.
Perhaps the effect of the crash couldve been eased if the government had stepped in to do something. History with 30 billion lost in market value a sum that would be worth 396 billion in 2018. By December 1935 the stock market DJIA had only recovered to 140 from its 1932 bottom -- still down a whopping 64 from its October 1929 peak.
In August 1929 just weeks before the stock market crashed the Federal Reserve Bank of New York raised the interest rate from 5 percent to 6 percent. As might be expected interest rate sensitive equities were also decimated during the Great Crash of 1929. A lot of people have been questioning if we will experience another stock market crash in the near future.
On Black Monday October 28 1929 the Dow Jones Industrial Average declined nearly 13 percent. Even though stocks cratered in the 1929 crash government bonds were safe havens for investors. It was the most devastating stock market crash in the history of the United States when taking into consideration the full extent and duration.
The decreased role of government is quite obvious in the aftermath of the crash. The example often cited is President Franklin D. Ultimately the cause of the 1929 Stock Market Crash was an asset and equity bubble driven by the general publics unrestricted access to credit.
 Great Depression Causes Of The Decline Britannica
Great Depression Causes Of The Decline Britannica
 The Stock Market Crash Of 1929 Stock Market Crash Stock Market Stock Market History
The Stock Market Crash Of 1929 Stock Market Crash Stock Market Stock Market History
 October 29 1929 Black Tuesday Stock Market Crash Constituting America
October 29 1929 Black Tuesday Stock Market Crash Constituting America
 Documents That Changed The World Delayed Stock Market Ticker Tape October 1929 Uw News
Documents That Changed The World Delayed Stock Market Ticker Tape October 1929 Uw News
 Goldman Sachs Commemorates 150 Year History The New York Stock Market Crash Of 1929 Preludes The Great Depression
Goldman Sachs Commemorates 150 Year History The New York Stock Market Crash Of 1929 Preludes The Great Depression
Why The 1929 Stock Market Crash Could Happen Again
Documentary Of The Week Stock Market Crash Of 1929 And The Great Depression
Stock Market Crash Of 1929 Causes Effects And Timeline
Stock Market Crash The Great Depression New Deal
 The Stock Market Crash Of 1929 And The Great Depression
The Stock Market Crash Of 1929 And The Great Depression
 The Stock Market Crash Of 1929 Us History Ii Os Collection
The Stock Market Crash Of 1929 Us History Ii Os Collection
 Stock Market Crash 1929 Definition Facts Timeline Causes Effects
Stock Market Crash 1929 Definition Facts Timeline Causes Effects
 Black Thursday American History Britannica
Black Thursday American History Britannica
 10 Facts To Know About The Stock Market Crash Of 1929
10 Facts To Know About The Stock Market Crash Of 1929
 Can The Government Control A Stock Market Crash Howstuffworks
Can The Government Control A Stock Market Crash Howstuffworks
What Is A Stock Market Crash Causes Consequences And How To Prepare
/wall-street-crash-78075346-08e95275110a4afd80681699e5d72bcb.jpg) Stock Market Crash Of 1929 Definition
Stock Market Crash Of 1929 Definition


Post a Comment for "What Did The Government Do About The Stock Market Crash In 1929"